RFID Library Tags for Book
Customized RFID library tags for accurate, efficient book tracking and inventory control.
Global Transformation Through RFID Library Technology: Real Case Studies from Singapore and Rotterdam
In today’s fast-paced digital world, public institutions must evolve to meet the expectations of tech-savvy communities. Libraries, as timeless centers of knowledge, are no exception. Across the globe, institutions are adopting RFID library systems to modernize book circulation, streamline operations, and enhance the user experience. What are the results? Faster borrowing, near-instant inventory, and stronger engagement with readers.
This article explores how RFID library technologies are revolutionizing public library systems through real-world deployments at the National Library Board (NLB) of Singapore and the Rotterdam Central Library in the Netherlands. These case studies highlight not only the implementation of library RFID tags and RFID book tags but also the broader impacts of automation, data, and intelligent systems on library management.
The Rise of RFID Library Solutions: A Global Trend
Traditional libraries have long faced challenges, including manual checkouts, delayed returns, slow inventory checks, and resource mismanagement. As the volume of library collections increases and user demand grows, legacy systems can no longer keep up. The introduction of RFID library solutions represents a significant leap forward, automating manual processes, improving efficiency, and reducing human error.
At the heart of these systems are RFID book tags—small, durable chips embedded into books and other media. These passive radio-frequency identification tags can be scanned wirelessly, without direct contact or line of sight, making them ideal for high-traffic, high-volume environments such as public libraries.
Case Study 1: National Library Board (NLB) of Singapore – Pioneering RFID in Libraries
Overview
As one of the earliest adopters of RFID in the public sector, the National Library Board (NLB) of Singapore implemented a full-scale RFID library system as early as 2003. With over 25 public libraries under its management and millions of materials in circulation, NLB required a scalable and reliable system to enhance its service delivery and reduce operational complexity.

RFID Library System Architecture
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| RFID Tag Type | HF 13.56 MHz, ISO 15693-compliant library RFID tags |
| Readers & Antennas | Located at self-checkout kiosks, book return stations, and exit gates |
| Self-Service Terminals | RFID-enabled for multi-item borrowing and returning |
| Automated Book Drops | 24/7 return kiosks that log returned books in real time |
| Automated Sorting Systems | RFID-powered conveyors that sort items by genre or category |
| Inventory Tools | Handheld HF RFID readers used for real-time shelf audits |
| System Integration | Seamless link to NLB’s Library Management System (LMS) |
Core Features and Use Cases
- Self-service borrowing & returns: Borrowing time reduced from 10–15 seconds per item to 2–4 seconds.
- Automated sorting: Returned items are automatically routed into the correct bins.
- Loss prevention: RFID gates trigger alerts for unissued books.
- Inventory management: Full stocktaking reduced from weeks to one day.
- Analytics and planning: Transaction data drives smarter procurement and shelving strategies.
Impact Metrics (Before vs After RFID)
| Metric | Before RFID | After RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Borrow/Return Time | 10–15 sec/item | 2–4 sec/item |
| Self-Checkout Adoption | Low | >90% usage |
| Inventory Audit Time | Weeks | 1 Day |
| Manual Labor Needs | High | Reduced by 40% |
| User Satisfaction | Moderate | Strongly Improved |
Library RFID tags have become central to the success of NLB’s operations, supporting automation at nearly every service touchpoint.
Case Study 2: UHF RFID at Rotterdam Central Library – Speed and Scalability
Overview
The Rotterdam Central Library is a hub of activity and innovation in the Netherlands, managing thousands of books and patrons daily. Unlike Singapore’s use of HF RFID, Rotterdam adopted UHF RFID technology, which offers longer read distances and accurate bulk scanning for high-speed inventory and logistics management.
UHF RFID Library System Setup
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| RFID Tag Type | UHF (860–960 MHz), EPC Gen2, ISO 18000-6C compliant RFID book tags |
| Tag Placement | Inside book covers and on non-metal areas of media |
| Fixed Readers | Installed at entrances, AMH systems, and self-check stations |
| Mobile Readers | Handheld UHF readers for high-speed scanning from up to 6 meters |
| Smart Book Trolleys | RFID-enabled carts that scan as they move through shelves |
| Software | Integrated with OCLC Wise LMS for real-time data updates |
Core Advantages and Features
- Fast shelf inventory: Scan entire shelves in seconds without pulling books out.
- Bulk self-checkout: Patrons can check out multiple items at once in under 2 minutes.
- Real-time loss prevention: Exit gates detect unauthorized removals instantly.
- Automated returns: Books dropped into smart bins are auto-sorted by category.
- Staff efficiency: Staff shift from manual checkout to patron engagement and programming.
Why UHF?
| Feature | HF RFID | UHF RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 13.56 MHz | 860–960 MHz |
| Read Range | 10–30 cm | 2–6 meters |
| Multi-Tag Reading | Moderate | Excellent |
| Inventory Speed | Medium | Very Fast |
Results After UHF RFID Adoption
| Metric | Before RFID | After UHF RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Audit Cycle | Biweekly | <1 Hour per floor |
| Average Borrowing Time | 6–8 minutes | Under 2 minutes |
| Staff Time | Spent on checkout | Reallocated to events and support |
| Shelf Accuracy | Manual detection | Automated alerts |
| Patron Engagement | Neutral | +12% footfall increase |
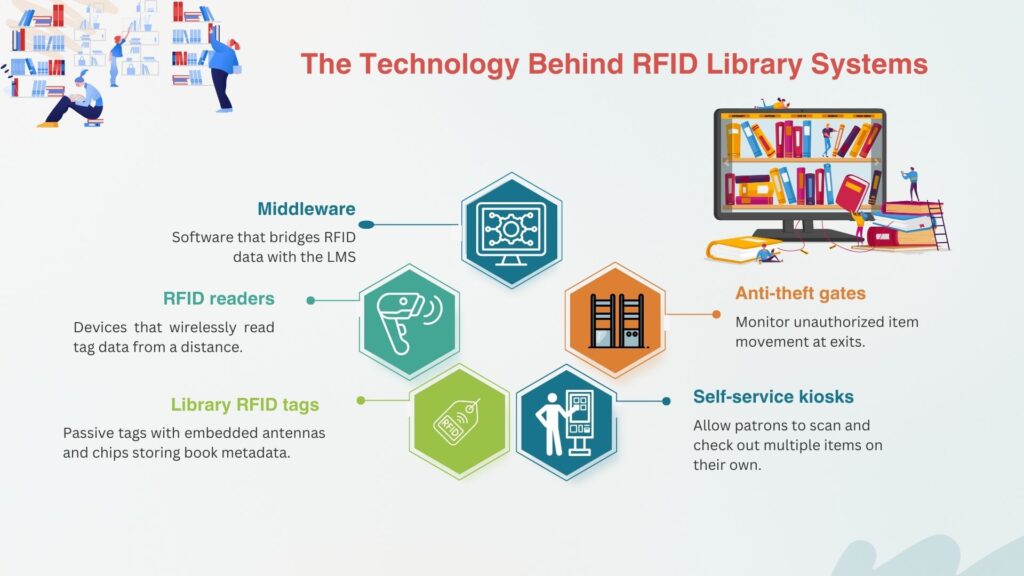
The Technology Behind RFID Library Systems
Whether using HF or UHF, every RFID library system relies on a similar set of technologies:
- Library RFID tags: Passive tags with embedded antennas and chips storing book metadata.
- RFID readers: Devices that wirelessly read tag data from a distance.
- Middleware: Software that bridges RFID data with the LMS (Library Management System).
- Anti-theft gates: Monitor unauthorized item movement at exits.
- Self-service kiosks: Allow patrons to scan and check out multiple items on their own.
Modern library RFID tags are durable, reprogrammable, and can endure thousands of borrowing cycles. HF tags are commonly used due to lower cost and shorter range, while UHF tags are preferred for fast scanning and bulk reading.
Whether using HF or UHF, every RFID library system relies on a similar set of technologies:
- Library RFID tags: Passive tags with embedded antennas and chips storing book metadata.
- RFID readers: Devices that wirelessly read tag data from a distance.
- Middleware: Software that bridges RFID data with the LMS (Library Management System).
- Anti-theft gates: Monitor unauthorized item movement at exits.
- Self-service kiosks: Allow patrons to scan and check out multiple items on their own.
Modern library RFID tags are durable, reprogrammable, and can endure thousands of borrowing cycles. HF tags are commonly used due to lower cost and shorter range, while UHF tags are preferred for fast scanning and bulk reading.
Key Benefits of RFID Library Systems
📦High-Speed Inventory Management
Staff can conduct full shelf audits in minutes rather than weeks using handheld readers or RFID-enabled trolleys. This reduces mis-shelving and helps maintain up-to-date records.
🧑🏫Reduced Staff Workload
By automating checkouts, returns, and shelf scanning, librarians can focus on patron engagement, event programming, and educational services.
🧠Data-Driven Decision Making
RFID systems provide usage analytics, helping libraries decide which genres to promote, which collections need expansion, and where bottlenecks occur.
🔒Loss Prevention
RFID gates and real-time alerts prevent unauthorized removal of items, reducing shrinkage and ensuring collection integrity.
🚀Enhanced Patron Experience
Self-service kiosks reduce queues, automate returns, and increase transaction speed, encouraging more people to use the library more often.
Global Innovators: Bibliotheca and the Scottsdale Public Library Case
In addition to Singapore and Rotterdam, Bibliotheca, a Swiss-based leader in RFID library solutions, has supported libraries worldwide in modernizing their services. A notable example is the Scottsdale Public Library in Arizona, USA.
Serving over one million visitors annually, Scottsdale sought to enhance its service delivery and embrace automation. With Bibliotheca’s support, the library transitioned its entire collection to library RFID tags, installed a new automated materials handler (AMH), implemented self-checkout kiosks, and upgraded its security systems. This transformation not only improved operational efficiency but also aligned the library with modern user expectations, demonstrating that the impact of RFID book tags is truly global.
Future of RFID in Libraries
Looking ahead, RFID library systems are poised to integrate with broader smart infrastructure:
- IoT Connectivity: Sensors and RFID data linking to cloud platforms for real-time analytics.
- AI-Driven Book Recommendations: Based on borrowing history via RFID logs.
- Mobile App Integration: Patrons can scan RFID books with smartphones for instant info.
- Smart Navigation: RFID-powered wayfinding within large libraries.
From physical book tracking to immersive digital experiences, library RFID tags will continue to be central in making libraries smarter, faster, and more accessible.
Choose the Right RFID Library Tags for Smarter Book Management
Discover how our advanced RFID book tags and library RFID solutions can streamline your inventory, enhance security, and improve patron experience. Contact our specialists today to discuss the correct RFID setup for your library and take your library operations to the next level.