Related Blog
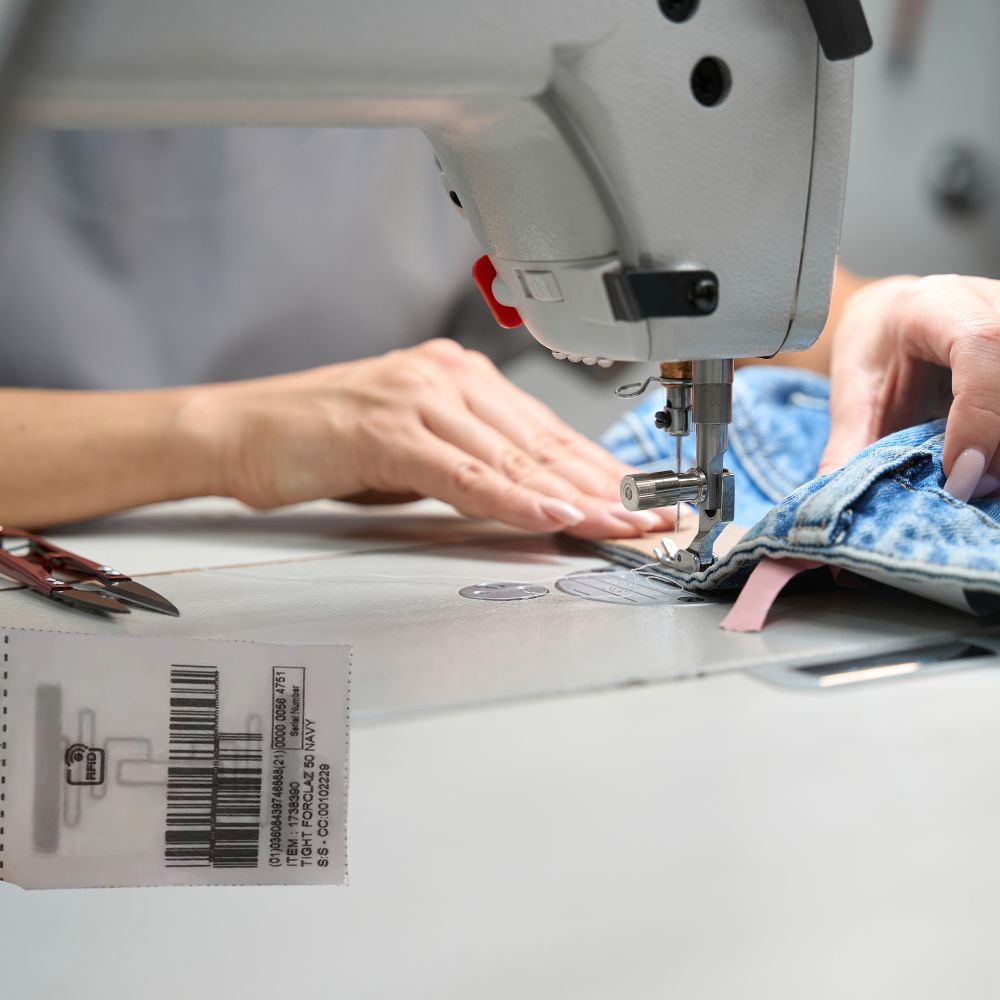

How to Remove RFID Security Tags from Clothes
This article explores effective and safe methods for removing security tags from clothing.

What Are the Benefits of RFID Technology in Healthcare
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is transforming the healthcare landscape, offering innovative RFID solutions to enhance patient safety and streamline operations.

How to Get RFID Tags for Cattle
This article provides a comprehensive guide on acquiring RFID and EID tags for cattle, specifically focusing on our products and USDA guidelines.