Related Blog

RFID vs NFC: Which Technology Suits Your Business Best?
Are you curious about the difference between RFID and NFC? In our rapidly evolving world, choosing the right contactless system can revolutionize daily operations in Retail, Logistics and Supply Chain, Transportation and Parking Management, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Asset Management and Security, Agriculture and Livestock Management, Education and Library Management, and Apparel and Textiles.

How to Remove RFID Sticker Adhesive off Headlight
This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide on safely and effectively removing RFID sticker adhesive from your vehicle headlight.
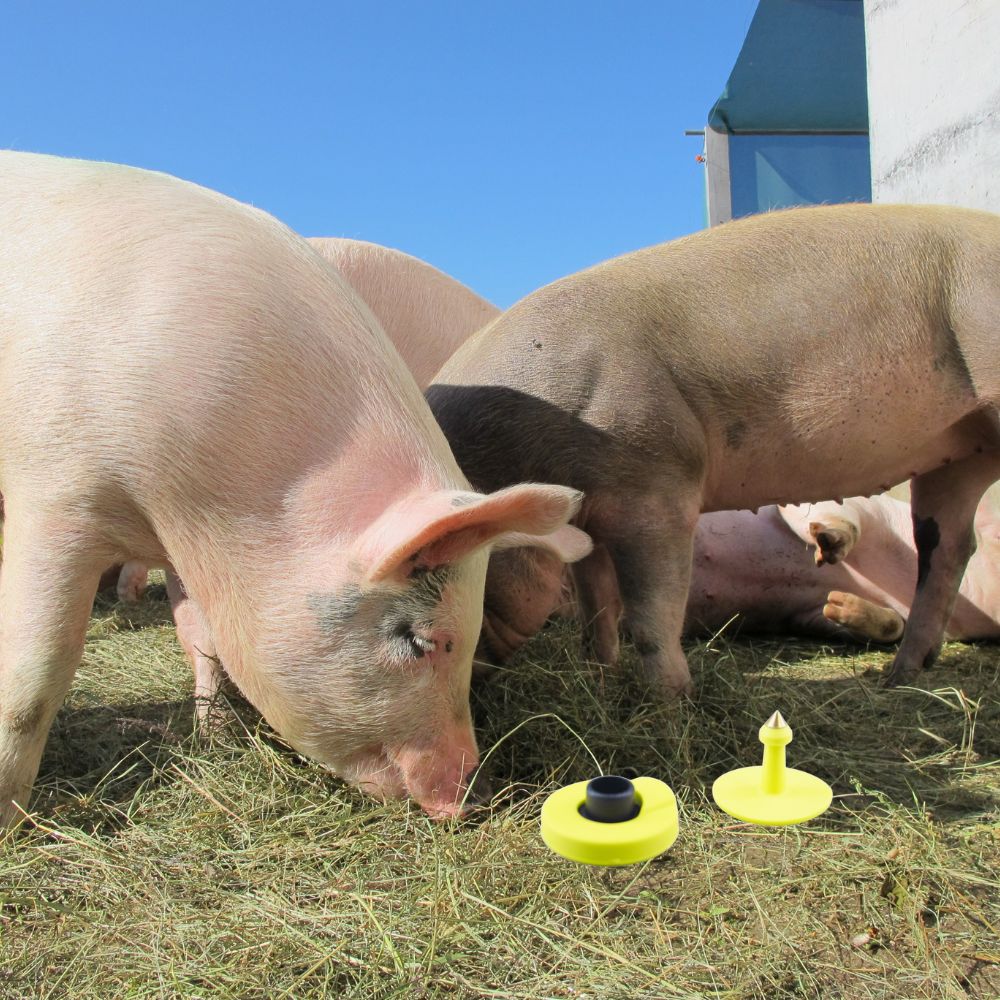

The Difference Between RFID and EID Tag
This article provides a comprehensive guide on the differences between RFID and EID tags, focusing on their applications in livestock management, particularly for cattle.