Related Blog

What is Radio Frequency Identification Technology
This article explores the transformative power of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology across various sectors.

Do You Need RFID Protection for Passport
With the rise of digital technology, concerns about data security have grown, particularly regarding passports and credit cards.
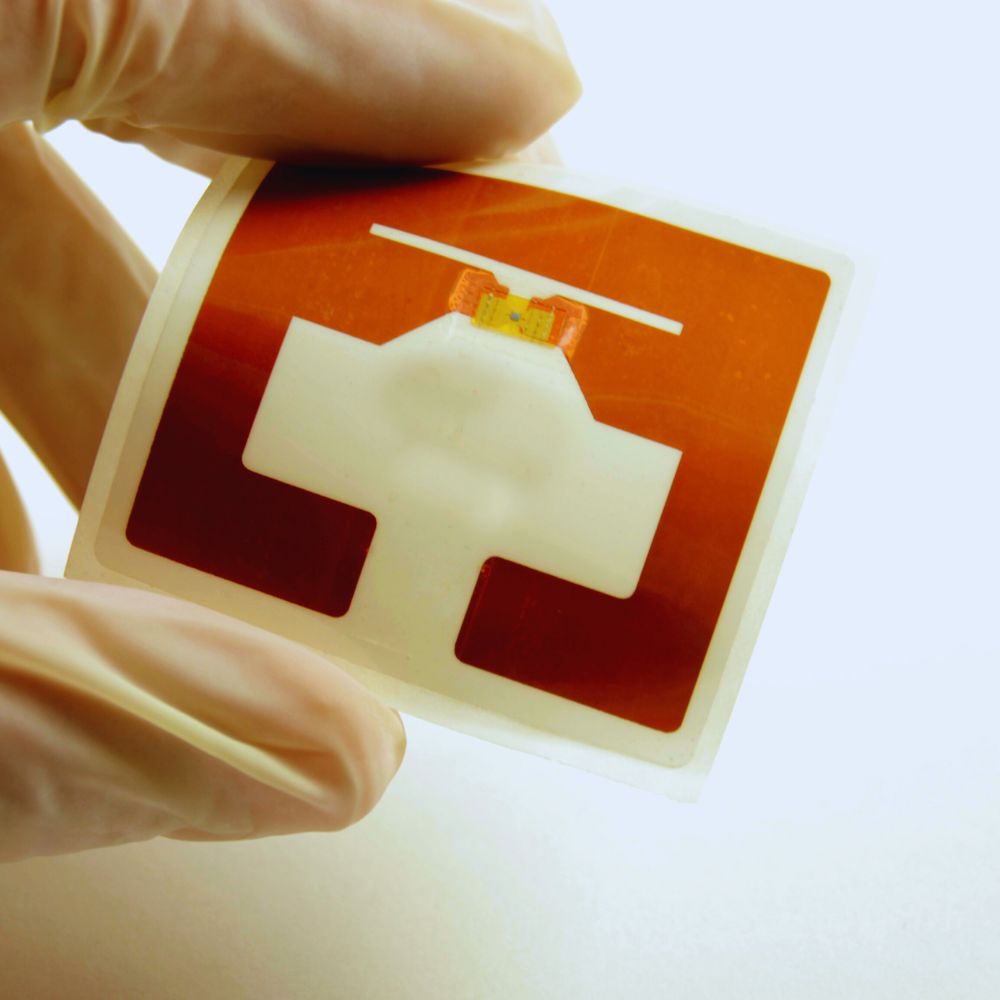

How Do Passive RFID Tags Work
Passive RFID tags work wonders in modern industries, from retail to logistics and supply chain operations. These small yet powerful tags rely on radio-frequency identification for asset tracking and inventory management tasks and even enhance security in high-stakes environments.