Related Blog

What is The RFID Inventory System
Understanding inventory management is essential for businesses across Retail, Logistics and Supply Chain, Transportation and Parking Management, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Asset Management and Security, Agriculture and Livestock Management, Education and Library Management, and Apparel and Textiles industries.

Is 13.56MHz NFC or RFID
If you’ve ever tapped a MetroCard, waved an office badge, or paid with your phone, you’ve already used 13.56 MHz technology — whether you knew it or not.
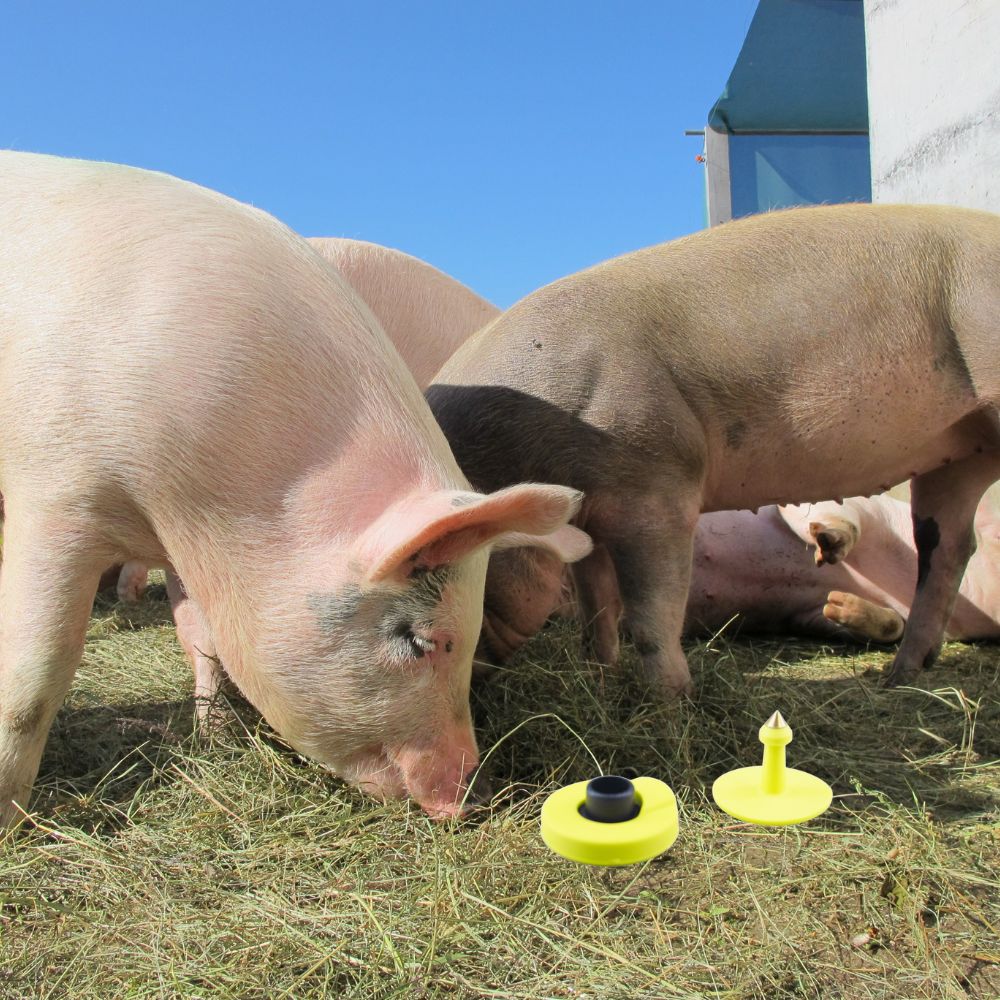

The Difference Between RFID and EID Tag
This article provides a comprehensive guide on the differences between RFID and EID tags, focusing on their applications in livestock management, particularly for cattle.