RFID Passive Tag Labels for Logistic Warehouse Management
Streamline Your Operations with High-Performance Logistic RFID Tags
Our advanced RFID Passive Tag offers a superior solution for businesses seeking to optimize their tracking and inventory management processes. Leveraging the power of radio-frequency identification, these tags provide unparalleled efficiency and reliability and are designed to boost operational performance and reduce costs.
Whether you need to track physical assets across your supply chain or manage inventory in real-time, our RFID tag technology provides the solution you need to succeed. With our innovative designs, we make it easy to adopt cutting-edge technology and start seeing results immediately. Discover how our logistic RFID tags can transform your operations.
Understanding RFID Passive Tag Technology
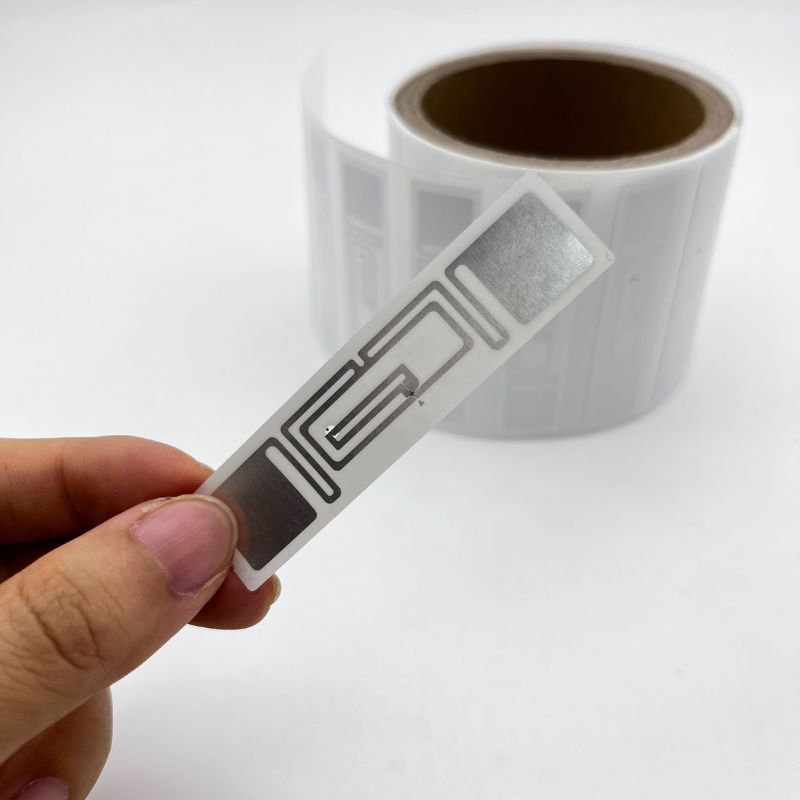
The core of our RFID Passive Tag solution lies in the sophisticated radio-frequency identification technology employed within each tag. RFID tags come in various types, each with its unique characteristics. Our product line includes passive RFID tags, which operate without an internal power source, instead relying on the energy transmitted by an RFID reader.
This energy powers the tag, transmitting signals back to the reader. On the other hand, an active RFID tag has its own internal power source, typically a battery, which enables it to transmit signals over longer distances and with greater power. Semi-passive RFID tags combine active and passive aspects, using a battery to power the tag’s internal circuits but not to broadcast a signal. The data stored on a tag is typically a unique identifier that links to a database with specific information about the tagged item.
The antenna within the RFID tag is a critical component that receives and transmits radio waves. Our passive RFID tags work by backscatter, sending a signal back to the reader when it is powered.
Active vs. Passive RFID Tags: Choosing the Right Fit
When choosing a radio-frequency identification tag, understanding the key differences between active and passive RFID tags is critical. The primary difference lies in the presence of an internal power source. Active RFID tags have a battery, making them capable of transmitting signals over a much longer read range.
Active tags are typically used in applications that need real-time location tracking over long distances, such as shipping containers or vehicles. However, the cost associated with active RFID tags is significantly higher than passive tags, and they also have a finite battery life. Passive RFID tags, on the other hand, do not have a battery and rely on the energy from an RFID reader to function.
While their read ranges may be shorter, passive tags are less expensive, have a longer operational life, and require less maintenance. Both active and passive tags are used to track items, but the choice depends on the business’s specific needs; for example, if your need is just like inventory management, you would likely choose passive tags because they are more cost-effective. These tags are suitable for asset tracking within warehouses and retail stores or any scenario that requires short-range identification. The difference depends on the tag’s application.
Optimizing Supply Chain with RFID Tracking
Implementing an RFID tracking system with our passive RFID tag can revolutionize your supply chain management. Using RFID technology, you can achieve real-time visibility of your assets as they move through the supply chain, from the warehouse to the customer.
These tags can improve tracking accuracy, reduce costs, and provide you with an easy-to-use system, especially with our reliable RFID reader and tracking software. Passive UHF tags can provide data, ensuring you can use RFID tracking for real-time data transfer.
Like an active RFID tag, an active tag might have a greater read range. However, they are far more expensive, making passive options the standard for most supply chain applications. Whether you need to track a single item or multiple items, our RFID tag lets you see where it’s located and how it’s moved within the chain.
Technical Specifications:
| Feature | Specification |
| Type | Passive RFID |
| Frequency | UHF (860-960 MHz) |
| Read Range | Up to 10 meters (dependent on reader and environment) |
| Material | Durable, weather-resistant plastic or metal, or inlay |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Compliance | EPC Gen2, ISO 18000-6C |
| Data Retention | Minimum 10 years |
| Adhesive | Strong, pressure-sensitive adhesive backing |
| Data Storage | Varies by tag type |
Usage Instructions:
Choose the appropriate tag: Select the RFID tag that best fits your application, environment, and tracking needs.
Attach the tag: Apply the RFID label to the item you want to track using the adhesive backing, ensuring the tag is securely attached.
Encode the tag: Use an RFID printer to encode the unique identifier onto the tag.
Implement an RFID Tracking system: Use an RFID reader and software to track your assets in real-time.
Monitor and manage: Leverage tracking data to optimize inventory and asset management processes.
Environmental Impact:
Our passive RFID tags are designed for durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. By eliminating the need for batteries, we also reduce our environmental footprint. We are committed to using sustainable practices in our manufacturing processes.
Get Your Custom RFID Tags
As a leading custom RFID tag manufacturer, we craft solutions based on the unique needs of your operation. We offer a wide range of customization options, including material, size, frequency, encoding, and read distance, ensuring each RFID Tag is perfectly customized to your requirements. No matter what application you use RFID tags for, we can provide rugged, reliable RFID tags that meet the highest quality and durability standards. Here are the main ways we customize RFID tags to fit your needs.

Material Selection
Material is key for customizing RFID tags. Plastic works in harsh conditions, while softer materials suit delicate spaces. Different materials also affect signal performance. Pick what fits your use case to ensure your tags last and work reliably.

Customized Size
Size shapes usability. Small tags fit tight spaces or tiny items, while larger tags are easily read. In crowded areas, sleek tags prevent clashes. Align shape and dimension with your goods for visibility, convenience, and performance.

Frequency Requirements
Choose LF, HF, or UHF based on read range, speed, and interference. LF and HF resist metals and liquids but have shorter ranges. UHF offers an extended range yet may face signal blocks. Match frequency to your environment for reliable performance.

Reading Distance
Define the distance at which you have to read the tag. Short distances work for retail checkouts, while warehouses may need meters of coverage. Antenna design, reader settings, and power outputs affect range.Adjust these factors to capture data accurately at the distance you need.

Encode
Plan how data is stored on each tag. Some only hold an ID, while others contain detailed info. Decide if you need a simple EPC or added user memory. Ensure your chosen format works with existing software. Proper encoding streamlines processes and slashes errors.
Application Environment
Consider real-world conditions. Temperature swings, humidity, and chemicals can degrade tags. For outdoor use, opt for UV-resistant casings. In healthcare or food settings, ensure compliance with safety rules. Matching your tags to the environment maximizes their lifespan.
Related Products
Customize any RFID tags from our factory to meet your requirements.








