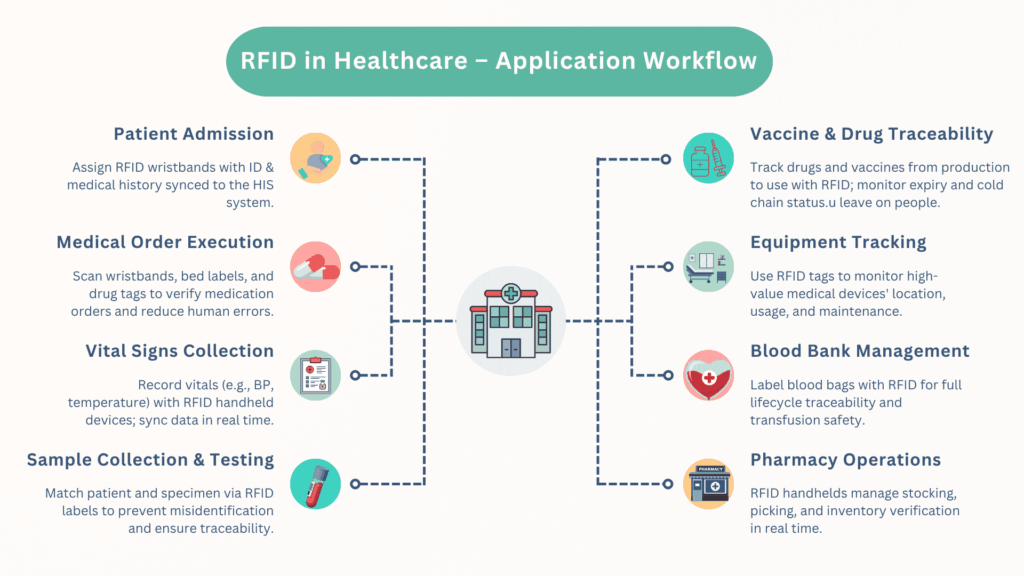
RFID in Healthcare
Healthcare RFID tags for patient tracking, medication management, and equipment monitoring.
RFID in Healthcare: Real-World Use Cases and Benefits of RFID Technology in Medical Environments
In an era where smart medical care is rapidly evolving, RFID in healthcare has emerged as a game-changing technology. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has enabled hospitals and healthcare providers to improve efficiency, accuracy, and patient safety drastically. Through real-time data collection, automatic identification, and secure information management, RFID technology in healthcare is transforming how facilities handle everything from admissions to medication dispensing.
This article explores the practical applications of RFID in healthcare, presenting real-world use cases, demonstrating the benefits of RFID in healthcare, and showcasing how healthcare RFID tags and devices support smarter, safer, and more cost-effective care.
What Is RFID in Healthcare?
RFID in healthcare involves using radio-frequency waves to identify and track objects or people automatically. RFID systems typically consist of:
- RFID tags: Embedded with unique IDs and data attached to patients, medications, equipment, etc.
- RFID readers or handheld devices: Scan and transmit data wirelessly to a central system.
- Data systems: Integrate with hospital information systems (HIS), lab systems, and supply chain platforms.
The combination of these components enables healthcare staff to access, monitor, and manage critical medical data in real time — a capability that is essential in today’s high-stakes healthcare environments.

Real-World Use Cases of RFID Technology in Healthcare
Let’s look at how RFID for healthcare is actively being implemented in different scenarios across hospitals and medical institutions:
1. Patient Admission and Identification
Upon arrival, patients are issued RFID-enabled wristbands containing their identification and medical history. Nurses or admission staff scan the wristband using RFID handheld devices to synchronize the data with the Hospital Information System (HIS) in real-time. This ensures accurate and consistent tracking of the patient across all departments.
✅ Benefits:
- Streamlines the admission process
- Minimizes patient identification errors
- Enhances data accuracy and traceability
2. Medical Order Execution and Medication Safety
Medication administration is a critical touchpoint where errors can have serious consequences. Before administering medication, healthcare staff use RFID readers to scan the patient’s wristband, medication packaging, and bed label. This verifies that the right patient is receiving the correct dose at the proper time.
✅ Benefits of RFID in healthcare include:
- Ensures adherence to prescribed treatment
- Reduces human errors
- Improves patient safety and compliance
3. Vital Signs Monitoring and Nursing Efficiency
Collecting and recording patients’ vital signs is a routine yet vital activity. With RFID handheld devices, nurses can capture and synchronize physiological data, such as temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure, directly into the hospital system. This simplifies nursing workflows and enables better decision-making.
✅ RFID in healthcare applications:
- Accurate real-time data logging
- Less manual paperwork
- Higher diagnostic precision
4. Vaccine Traceability and Cold Chain Monitoring
Using RFID technology in healthcare, each vaccine vial can be tracked from manufacturing to administration. RFID tags contain data about origin, expiration, and storage conditions. During transport and handling, RFID devices record environmental data, including temperature and location.
✅ Benefits:
- Full lifecycle traceability
- Reduces counterfeit vaccines
- Enhances public health safety
5. Drug Inventory and Traceability
Hospitals and pharmacies use RFID healthcare tags on drug packaging to track inventory levels, expiration dates, and batch numbers. Pharmacists scan tags during dispensing to ensure that the correct medications are given and expired items are removed from inventory.
✅ Results:
- Real-time drug inventory visibility
- Faster recalls of faulty batches
- Increased regulatory compliance
6. Smart SPD Material Management
The SPD (Supply, Processing, and Distribution) model benefits significantly from the use of RFID. Medical materials such as gloves, IV fluids, and surgical supplies are tagged and tracked from central warehouses to clinical units. RFID handheld terminals help achieve zero-inventory management.
✅ Advantages of RFID for healthcare here:
- Reduces wastage and stockouts
- Saves operational costs
- Streamlines the supply chain
7. Pharmacy Sorting and Replenishment
RFID simplifies warehouse and in-store pharmacy operations. As items are received, RFID readers scan drugs and shelf barcodes to guide shelving and inventory checks. During replenishment, RFID devices verify the correct placement, pricing, and expiration dates.
✅ Benefits of RFID technology in healthcare:
- Minimizes picking errors
- Speeds up shelf restocking
- Keeps inventories accurate and compliant
8. Blood Bank and Sample Management
Blood bags and patient samples are extremely sensitive and must be matched precisely to ensure accurate results. RFID wristbands and specimen labels ensure accurate sample-to-patient mapping. RFID handheld devices track each step — from collection to testing to transfusion.
✅ Critical RFID healthcare functions:
- Eliminates sample mix-ups
- Tracks blood from donor to patient
- Enhances lab processing time and safety
9. Medical Waste Tracking
To ensure environmental safety and compliance, RFID tags are attached to medical waste containers. These tags contain metadata about the waste type, location, time, and staff member responsible. RFID readers scan and log this data in real-time.
✅ Benefits of RFID in healthcare waste management:
- Ensures proper disposal practices
- Tracks volume and waste categories
- Reduces legal and safety risks
10. Valuable Equipment Tracking
Hospitals use RFID technology to monitor the location and usage of expensive medical instruments like endoscopes, surgical robots, and imaging equipment. RFID labels affixed to the assets allow for real-time location tracking and usage logs.
✅ Advantages of healthcare RFID tags:
- Prevents equipment loss
- Improves utilization rates
- Increases accountability and asset lifespan
How RFID Handheld Devices Drive Smart Healthcare
At the heart of these use cases are RFID handheld terminals, which integrate RFID readers with Wi-Fi, barcode scanners, and user authentication systems (e.g., fingerprint logins). These smart devices allow mobile, real-time access to medical data — whether in a ward, operating room, pharmacy, or warehouse.
Key functionalities include:
- Instant identification of patients and items
- Mobile query access to HIS/LIS systems
- Secure login based on user role
- Remote data transmission for synchronization
With these features, RFID technology in healthcare delivers a management leap that improves both the quality of care and the efficiency of operations.
Benefits of RFID in Healthcare: Summary
| Area | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Patient Care | Accurate ID, reduced errors, better experience |
| Operations | Faster workflows, lower labor cost |
| Inventory | Real-time tracking, less waste |
| Safety | Enhanced traceability, higher compliance |
| Management | Smarter decisions, data-driven strategy |
The benefits of RFID in healthcare are both immediate and long-term, enabling cost savings, regulatory compliance, and service excellence.
Challenges to Consider
While the benefits are compelling, successful adoption of RFID for healthcare requires overcoming several challenges:
- Initial costs: RFID systems and devices may require significant upfront investment.
- System integration: RFID must work seamlessly with HIS, LIS, ERP, and other platforms.
- Training: Staff must be trained to operate RFID equipment correctly.
- Privacy: Patient data must be protected under HIPAA or regional data laws.
Healthcare institutions need a phased implementation plan and vendor partnerships to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion: RFID as the Engine of Smart Medical Care
The integration of RFID in healthcare is no longer experimental — it is a proven driver of smart medical transformation. By enabling automatic identification, precise data collection, real-time tracking, and secure access, RFID technology in healthcare bridges gaps in safety, efficiency, and quality.
As more hospitals embrace digital transformation, healthcare RFID tags, RFID handheld devices, and smart management systems will define the future of care. For healthcare providers looking to optimize processes, reduce risks, and enhance patient satisfaction, RFID for healthcare is not just an upgrade — it is an essential evolution.
Ready to Transform Your Healthcare Operations with RFID?
Whether you're looking to improve inventory management, patient care, or medical traceability, our experts are here to guide your digital transformation journey.
Applications of RFID in Healthcare
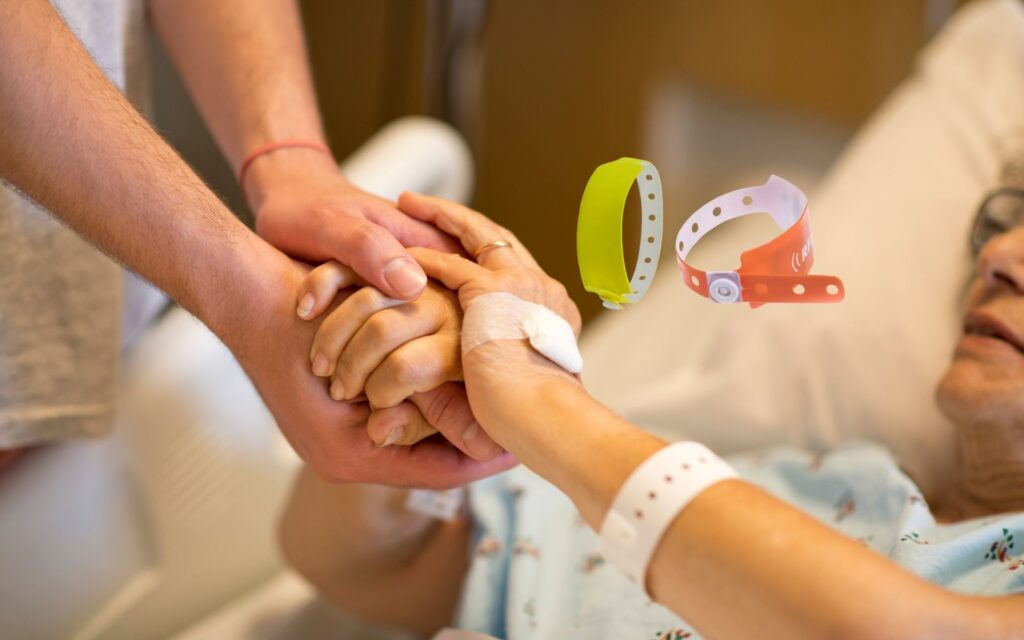
Patient Identification and Tracking
RFID wristbands are assigned to patients upon admission and contain essential personal and medical information. Healthcare providers use RFID readers to verify patient identity before administering medication, performing procedures, or transferring patients between departments. This reduces medical errors, prevents misidentification, and enhances patient safety.
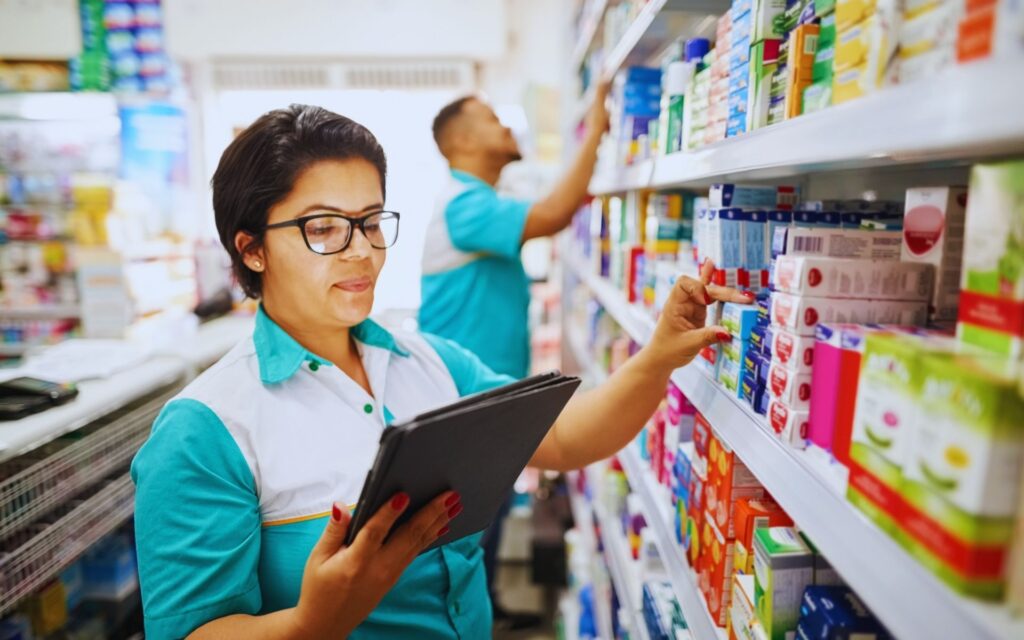

Medication Management
Hospitals use RFID tags on drug packaging to manage inventory, ensure correct dispensing, and monitor expiration dates. Pharmacists and nurses scan medications and match them with patient data to verify accuracy, reducing the risk of medication errors and improving treatment compliance.
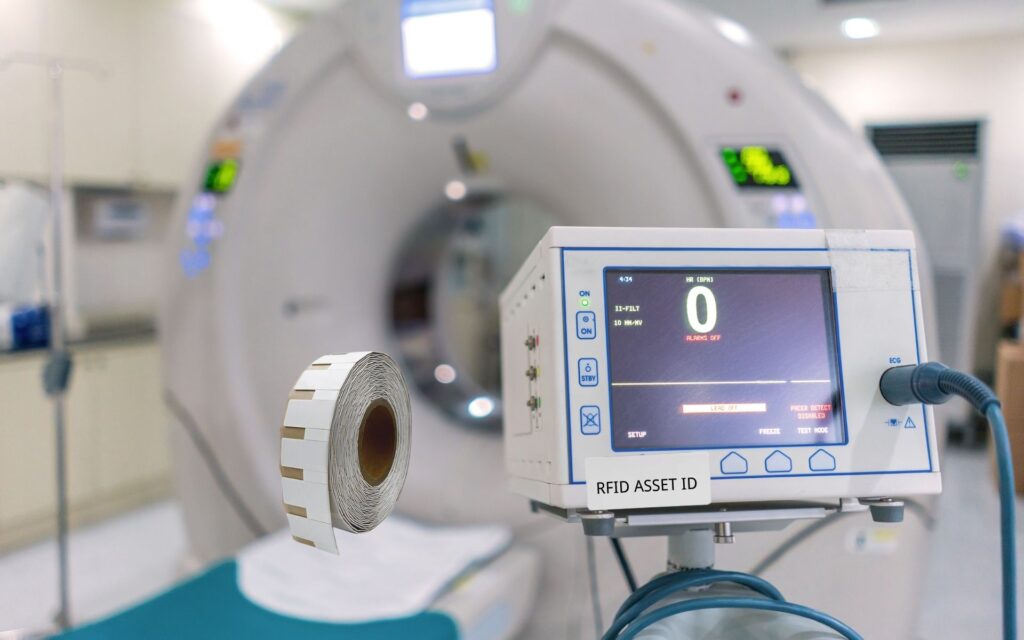
Medical Equipment Tracking
RFID tags are attached to valuable medical equipment like defibrillators, infusion pumps, and surgical instruments. This allows staff to locate equipment quickly, monitor usage, schedule maintenance, and prevent loss or theft. It also improves asset utilization and reduces downtime.
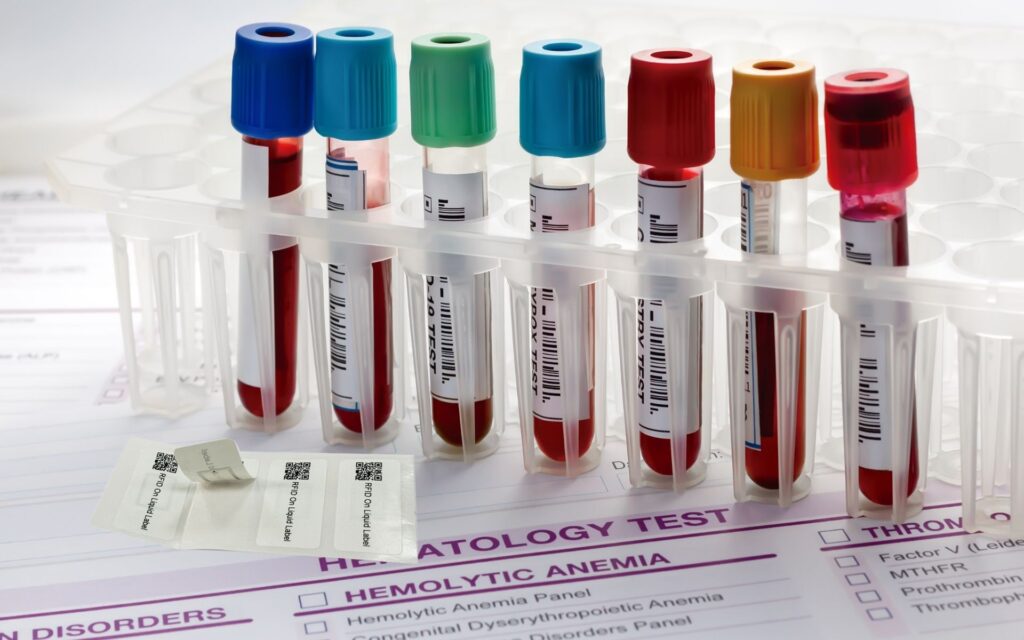
Sample and Specimen Management
During blood draws or lab testing, RFID labels are applied to vials and specimen containers to track them from collection to analysis. This ensures accurate patient-to-sample matching, reduces the risk of mix-ups, and supports faster and more reliable diagnostics.


