RFID Tire Tags for Tire Management
FID tire tags for accurate, efficient tire tracking, lifecycle monitoring, and inventory control across production and fleet operations.
Real Case Application of RFID Tire Tags: Revolutionizing Tire Management Across the Supply Chain
In today’s highly digitized automotive ecosystem, tire manufacturers and fleet operators are increasingly turning to RFID tire tag technology as a game-changer. These smart tire tags enhance efficiency, accuracy, safety, and cost control from production to end-of-life. Through real-world case applications and detailed implementation strategies, this article explores the value of RFID tire tag solutions, the different installation methods, and the robust traceability capabilities they provide.
What Is a Tire Tag and Why Is It Critical?
A tire tag refers to a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tag that is embedded, patched, or affixed to a tire, thereby granting it a unique digital identity. This identity functions as a lifelong ID card for the tire. Through RFID technology, RFID chips in tires can store and relay data such as:
- Brand, model, and manufacturing specifications
- Tire pressure and temperature readings
- Usage metrics like mileage and wear
- Maintenance and rotation history
- Transport and sales tracking information
As tire RFID adoption grows, traditional problems such as manual entry, barcode misreads, and a lack of traceability are being replaced by real-time automation, improved safety, and streamlined logistics.
Case Study: RFID Tire Tags in Global Supply Chain Management
Case Study: RFID Tire Tags in Global Supply Chain Management
A leading multinational tire manufacturer based in Germany has integrated RFID technology into its tires across its global operations. The company equipped all new production tires with embedded tire tags and then implemented RFID readers in its manufacturing plants, distribution centers, dealerships, and service centers.
Outcomes:
- Inventory time reduced by 85% in regional warehouses
- Shipping errors cut by 70% due to automated match verification
- Tire claims and recalls were traceable within minutes through digital history
- Fleet maintenance compliance increased due to automated alerts
This case exemplifies how RFID creates end-to-end digital transparency across the tire lifecycle.

Three Main Installation Methods for RFID Tire Tags
1. Embedded Tire Tags (In-Tire Tags)
Installation: Embedded directly into the tire during manufacturing, usually before vulcanization. A yellow stripe is typically used to identify RFID-enabled tires.
Use Case: Ideal for OEMs or large tire producers focusing on tire lifecycle management from factory to end-user.
Benefits:
- Permanent, tamper-resistant
- Fully protected from environmental damage.
- Enables full traceability from raw material to recycling
Example: Michelin embeds RFID tags in truck tires to track retreading cycles and optimize replacement intervals.
2. Patch-Type RFID Tire Tags
Installation: Applied after production using specialized adhesive, similar to repair patches, and chemically bonded to the tire’s inner wall.
Use Case: Common in aftermarket and fleet retrofitting scenarios.
Benefits:
- Easy to install during inspection or rotation
- Cost-effective for existing tire inventory
- Good durability for internal usage conditions
Example: A commercial bus fleet in Japan retrofitted 20,000 tires with patch-type RFID tire tags to automate their safety inspections.
3. Smart Labels (External RFID Tire Tags)
Installation: Printed and encoded via RFID-enabled barcode label printers, affixed externally to the tire or packaging during warehousing or transport.
Use Case: Widely used in logistics, distribution, and retail environments.
Benefits:
- Low cost and easy replacement
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Ideal for short-term identification and logistics processes
Example: A European tire distributor used smart RFID tags during Black Friday sales to coordinate warehouse and delivery logistics, reducing lost shipments by 40%.
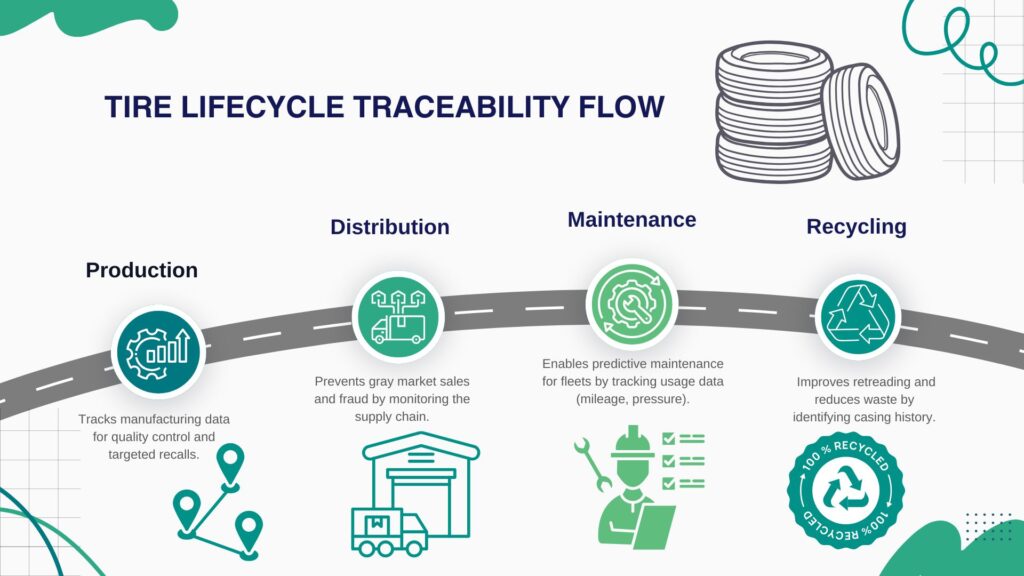
Tire Traceability: Tracking Every Step of the Journey
Traceability is one of the key features that make tire RFID technology essential.
1. Production-Level Traceability
Each RFID tire tag stores detailed manufacturing information:
- Raw material batch
- Assembly line operator ID
- Timestamped data from curing, mold, and balance testing
This allows real-time tracking and quality control. If a batch is defective, affected tires can be quickly located and recalled.
2. Distribution and Sales Tracking
During warehousing and transit:
- RFID readers at each node capture location and status updates.
- Unauthorized regional sales or dealer fraud can be identified instantly.
Example: A Chinese tire brand integrated RFID for logistics tracking, enabling it to reduce cross-region gray market sales and enforce fair pricing.
3. Usage Monitoring and Maintenance
Fleet operators install readers in service bays and vehicle axles. The RFID tire tag monitors:
- Mileage
- Air pressure and temperature
- Rotation dates
- Tread depth (via connected sensors)
A U.S.-based logistics firm uses RFID chips in tires for predictive maintenance across its 1,000-vehicle fleet, improving uptime by 30%.
4. End-of-Life and Recycling
RFID makes it easier to identify casing condition and service history during retreading or disposal, encouraging sustainability.
Example: Retreading plants use RFID scan history to sort viable casings, cutting waste by 25%.
RFID vs Traditional Barcode Systems in Tires
| Feature | Traditional Barcode | RFID Tire Tags |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Prone to wear and loss | Long-lasting and embedded |
| Data Capacity | Limited | Extensive and dynamic |
| Read Method | Line-of-sight | Non-line-of-sight |
| Traceability | Minimal | Full lifecycle visibility |
| Cost Over Time | Higher due to labor | Lower through automation |
RFID solves the problems inherent in manual tracking: no scanning angle is required, no wear-out occurs, and data remains intact even in rough environments.
Regulatory Landscape Supporting RFID in Tires
Global regulatory trends are accelerating RFID tire adoption:
- United States: FMCSA regulations promote tire safety and traceability in fleets
- EU: UNECE standards encourage digital labeling and lifecycle transparency
- China: Mandatory tire labeling policies include RFID integration in top-tier brands
These mandates further validate the tire tag as a vital tool for ensuring compliance, managing risk, and promoting sustainability.
Key Benefits of RFID Tire Tag Adoption
- Improved Safety – Real-time alerts on critical tire conditions
- Reduced Costs – Efficient inventory, automated tracking, and minimized errors
- Extended Tire Life – Data-driven maintenance scheduling
- Streamlined Recalls – Instant access to production and sales history
- Stronger Compliance – Alignment with industry regulations and labeling policies
- Sustainability Support – Promotes recycling and retreading efficiency
Conclusion
The implementation of RFID tire tags represents a pivotal advancement in the automotive and logistics industries. From embedded tags in tire manufacturing to smart labels for distribution and patch types for aftermarket integration, these innovations offer scalable solutions for every stage of the tire lifecycle. The ability to track, manage, and optimize tires via RFID chips in tires is no longer futuristic—it’s the new standard.
Whether you’re a manufacturer seeking improved quality control, a distributor requiring accurate inventory management, or a fleet manager focused on safety and cost efficiency, RFID-powered tire tags offer a proven, future-ready solution.
Upgrade your tire management today with RFID tire tags
Enhance safety, streamline operations, and ensure full traceability from production to the road. Contact us now to learn how RFID technology can transform your tire operations.


