Blog relacionado

¿Las etiquetas RFID son antirrobo?
Este artículo explora la eficacia de las etiquetas RFID como solución antirrobo en la industria minorista.

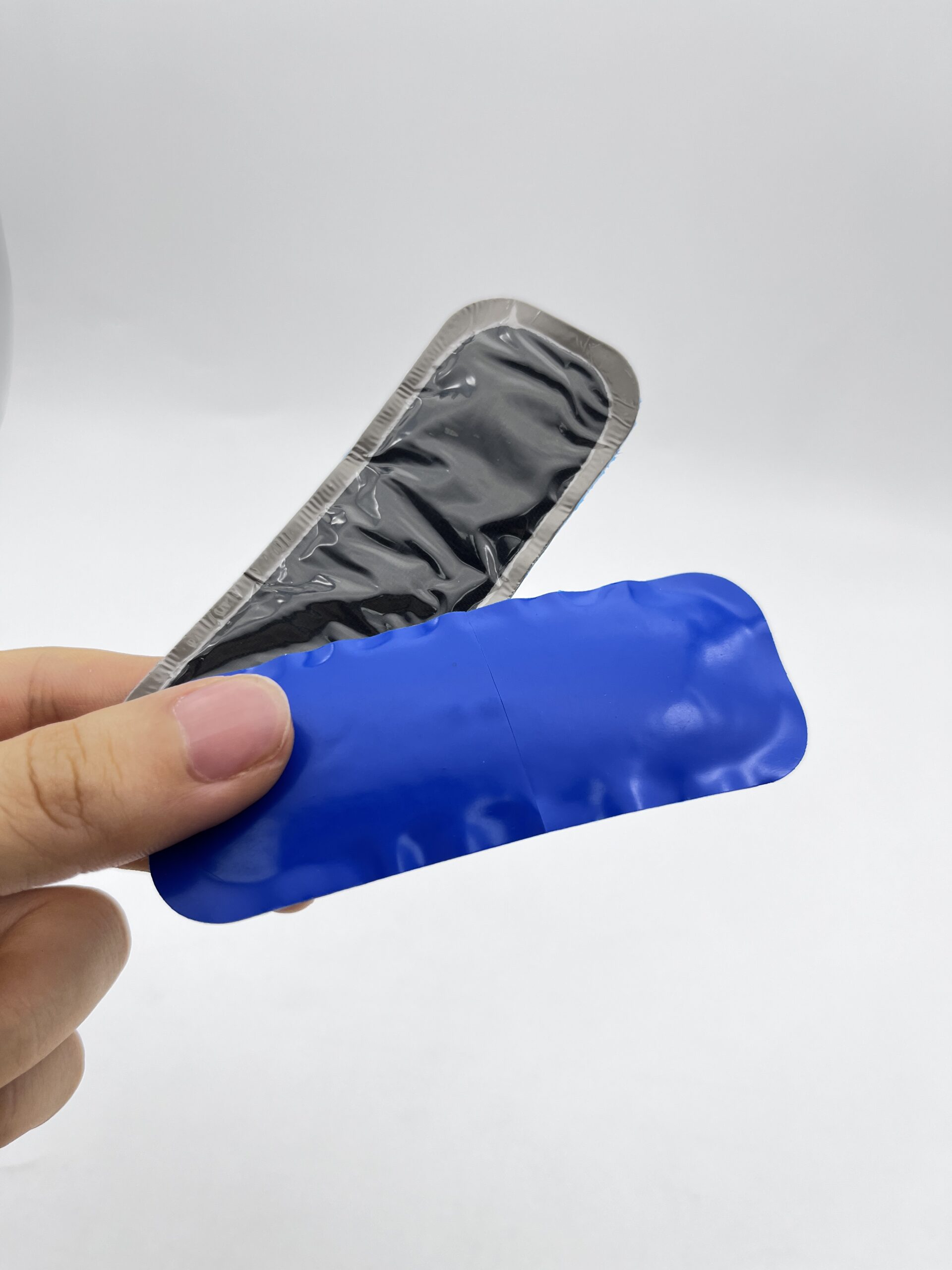
¿Qué es una etiqueta RFID?
Este artículo explora el fascinante mundo de las etiquetas de identificación por radiofrecuencia (RFID), dispositivos pequeños pero poderosos que están revolucionando el funcionamiento de las empresas.

¿Pueden las etiquetas RFID rastrear la ubicación?
Las etiquetas RFID se han convertido en herramientas indispensables para las empresas que buscan mejorar la eficiencia y la visibilidad en sus diversas operaciones. Si bien se las conoce comúnmente por su utilidad para la gestión de inventarios y la prevención de robos, surge una pregunta frecuente: ¿se pueden utilizar las etiquetas RFID para el seguimiento de la ubicación?