Related Blog

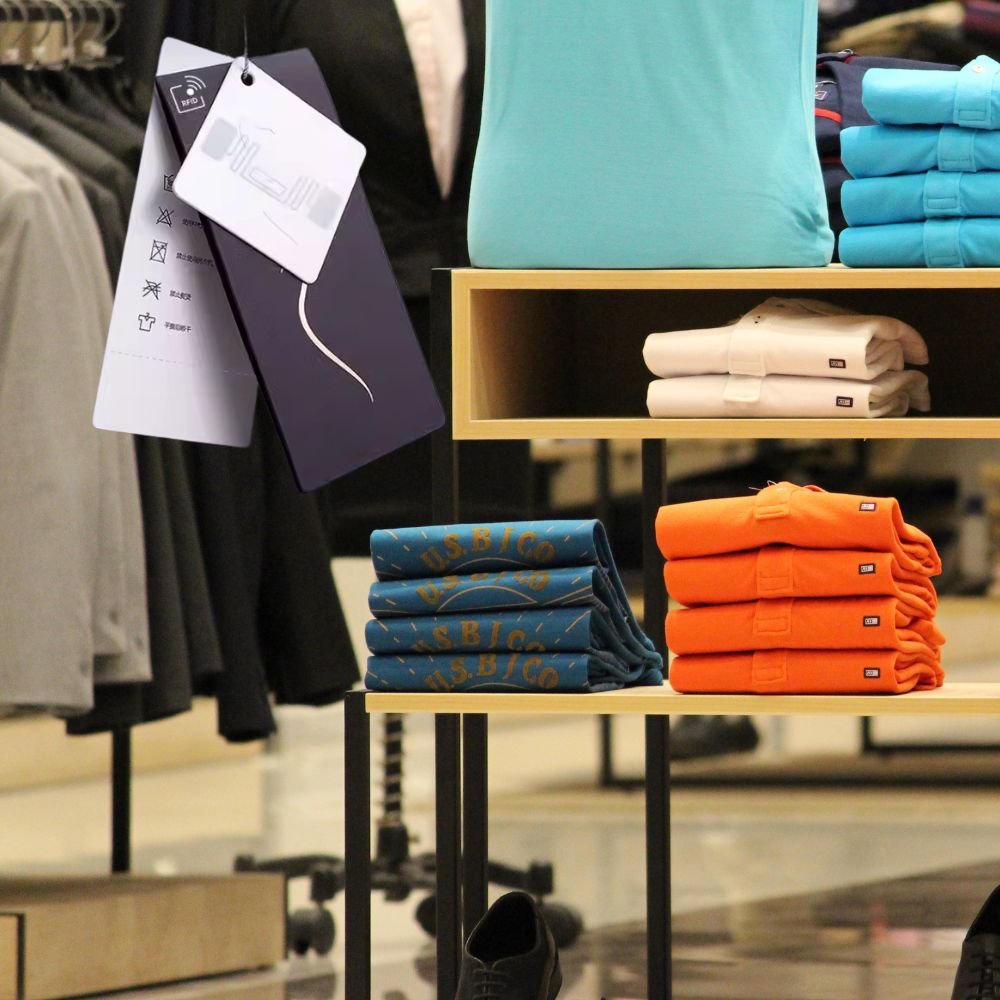
What Does RFID Stand for in Retail
Radio frequency identification (RFID stands for radio frequency) is a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track items with incredible precision.

How Does RFID Tag Work in a Warehouse
In the modern world of warehouse and inventory management, harnessing the power of RFID technology can automate time-consuming processes, making your entire operation more seamless and profitable.

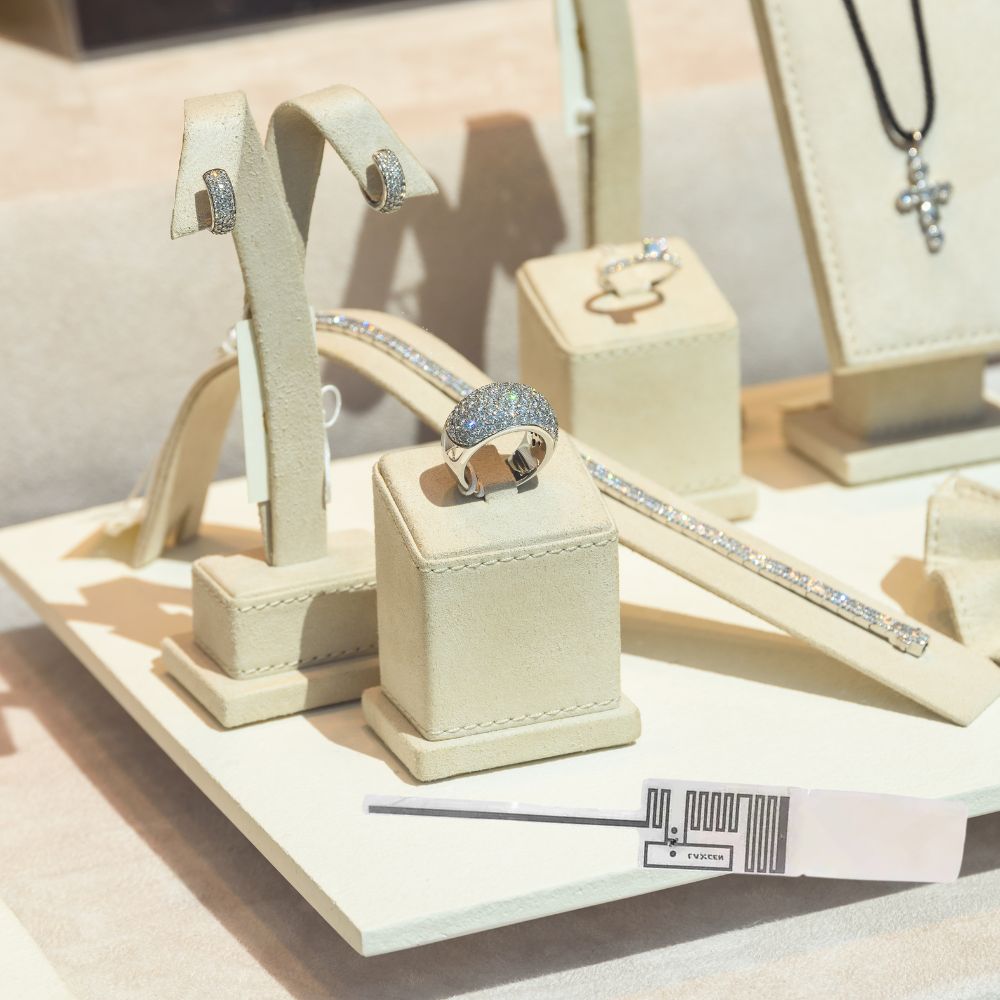
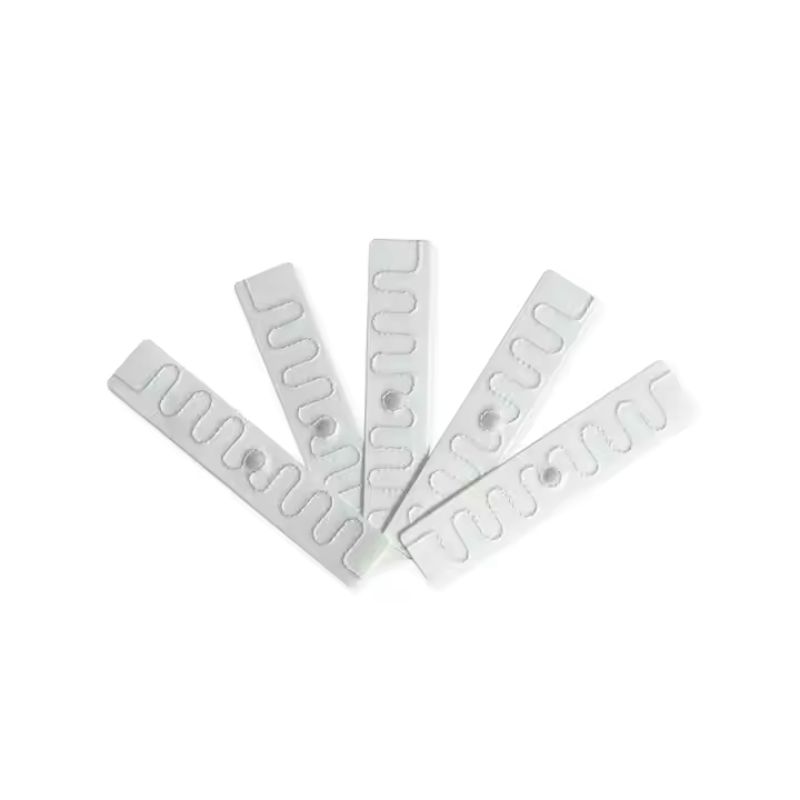
What is RFID Tag
This article explores the fascinating world of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags, small but mighty devices revolutionizing how businesses operate.