Blog relacionado
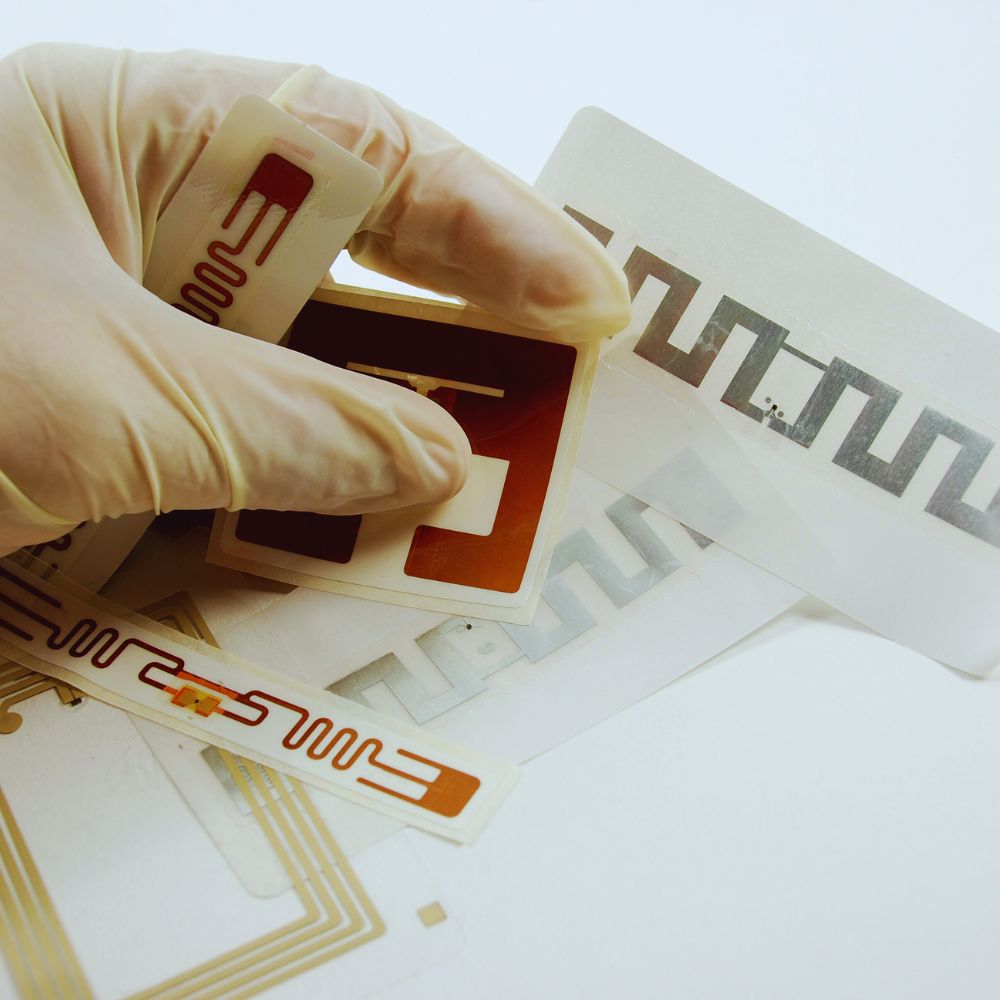

O que é etiqueta RFID
Este artigo explora de forma abrangente as etiquetas RFID, um tipo de etiqueta RFID que oferece uma maneira versátil e eficiente de implementar a tecnologia de identificação por radiofrequência.

Como funcionam as etiquetas RFID
Este artigo desmistifica o funcionamento interno da tecnologia RFID, concentrando-se em como as etiquetas RFID funcionam para transformar operações em diversos setores.

Quais são os três tipos de RFID
RFID—identificação por radiofrequência—é uma tecnologia sem fio notável que usa ondas de rádio para identificar e rastrear itens por meio de uma pequena etiqueta. Mas quais são os três tipos de RFID e por que eles são importantes para o seu negócio?