Related Blog

What are RFID Labels
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) labels revolutionize how businesses track and manage assets, inventory, and information. Unlike traditional barcodes, RFID tags use radio waves to wirelessly transmit data, offering a more efficient and versatile solution for various industries.
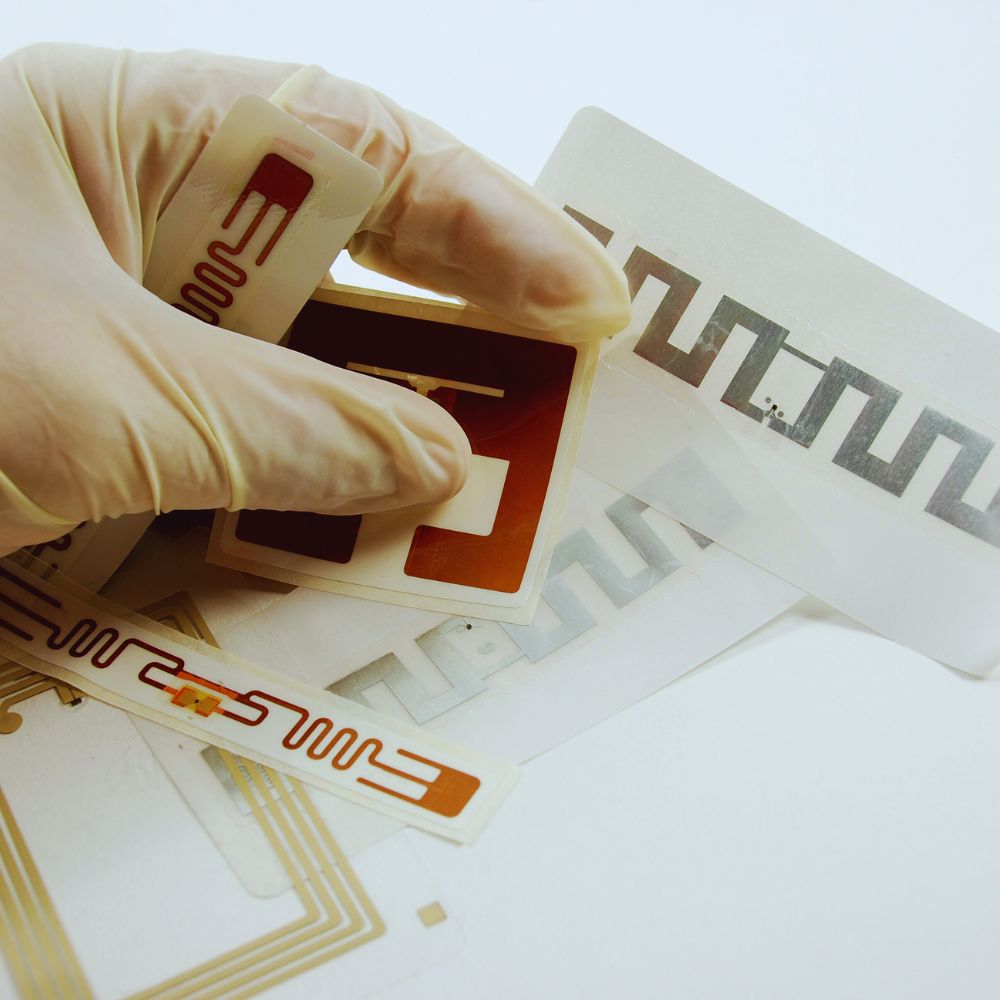

What is RFID Label
This article comprehensively explores RFID labels, a type of RFID tag that offers a versatile and efficient way to implement radio frequency identification technology.

What is Radio Frequency Identification Technology
This article explores the transformative power of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology across various sectors.












