Related Blog
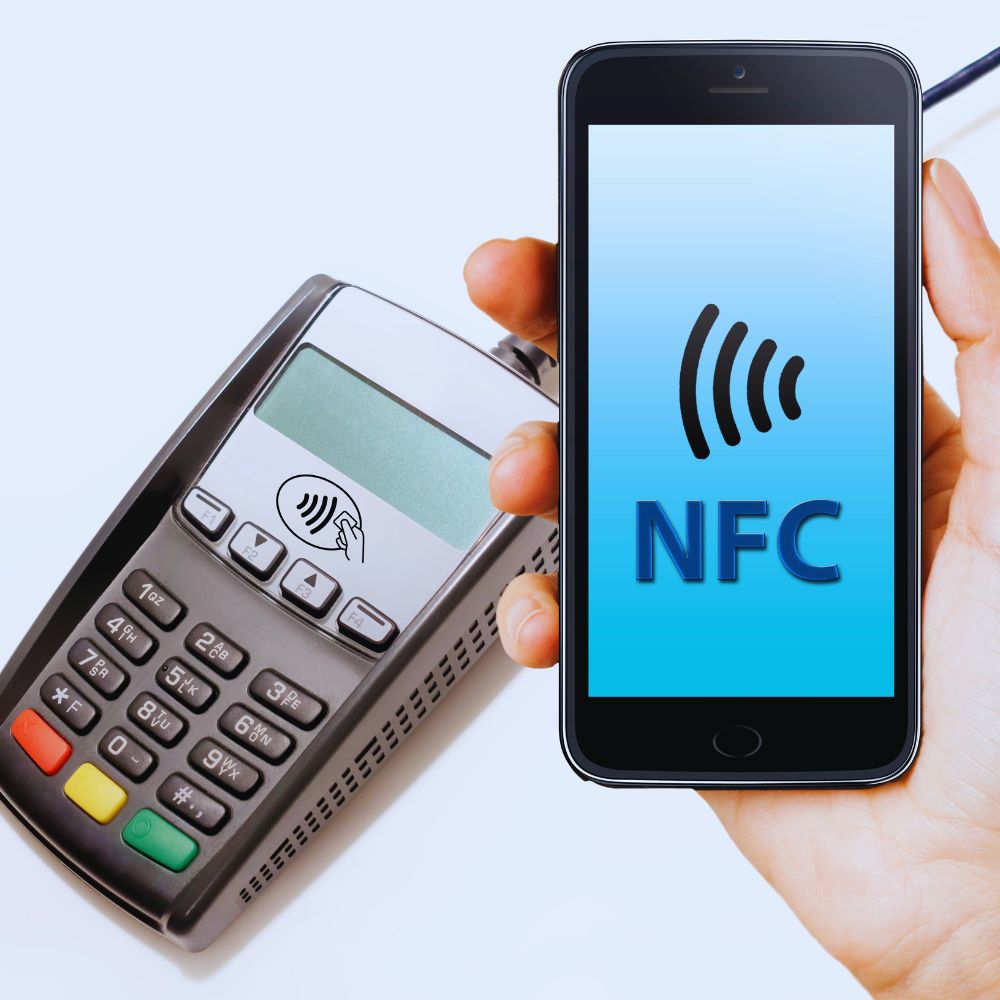

Can Android NFC Read RFID Tags
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags are increasingly prevalent in various applications, from inventory management to contactless payments. With the rise of NFC (Near Field Communication) in smartphones, a common question arises: Can Android phones with NFC capabilities read RFID tags?
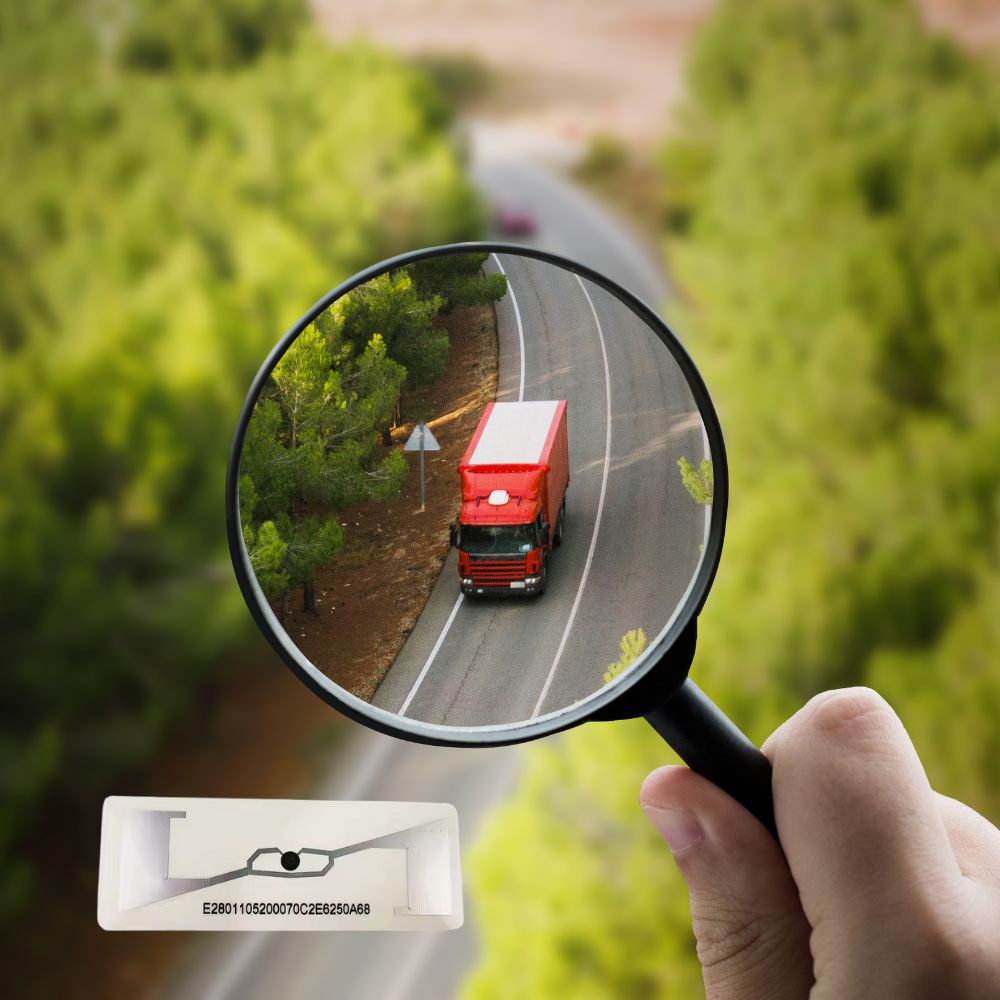

Can RFID Tags Track Location
RFID tags have become indispensable tools for businesses seeking to improve efficiency and visibility across various operations. While commonly known for inventory management and theft prevention, a frequent question arises: Can RFID tags be used for location tracking?
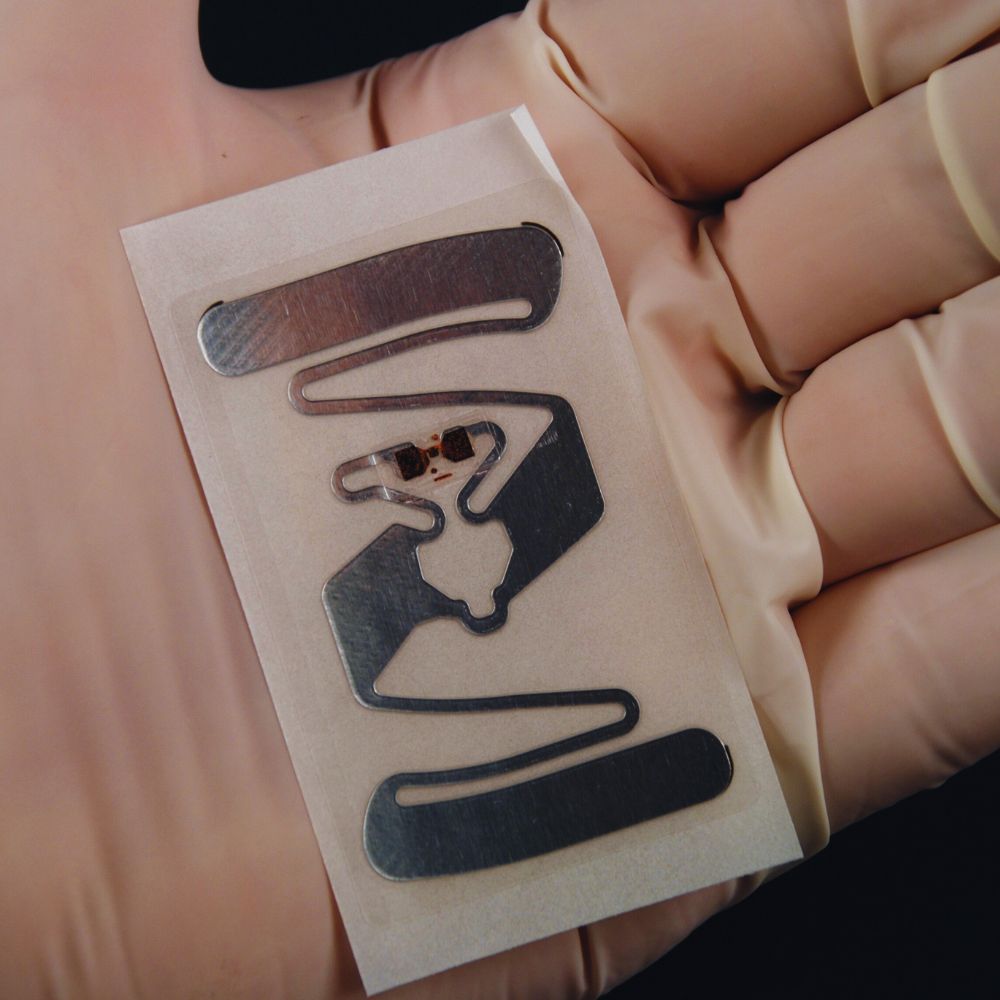

What is The Difference Between RF and RFID Tags
This article demystifies the often-confused technologies of RF (Radio Frequency) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), specifically focusing on RF tags and RFID tags.